Waste-to-Energy : WtE Industry Report: Growth amidst challenges

Since 2012 the Waste-to-Energy Industry Barometer takes a closer look at the state of the industry worldwide. ecoprog GmbH carried out the survey and the evaluation on behalf of CEWEP (Confederation of European Waste-to-Energy Plants). For the 2024 survey, ecoprog questioned around 500 operators of thermal waste treatment plants and more than 700 plant manufacturers and suppliers in the WtE industry worldwide.
The findings indicate that while WtE operators remain optimistic, broader industry sentiment is more cautious.
Optimism among WtE plant operators
Despite economic headwinds, the Waste-to-Energy (WtE) sector has shown resilience in 2024. Business development among WtE plant operators has improved, with a more positive outlook compared to the previous year. However, the overall mood in the industry remains more subdued than in 2023.
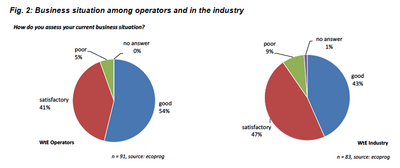
The business climate index for WtE plant operators rose to 91.7 points in 2024, up from 87.6 in 2023. A striking 95% of operators rated their current business situation as satisfactory or good. Plant utilization has also significantly increased, with 66% reporting high usage levels compared to 42% in the previous year. Looking ahead, optimism continues to grow, as only 20% of operators foresee worsening business conditions, a substantial improvement from 34% in 2023.
According to industry analysts at ecoprog, the positive trend underscores the ongoing shortage of disposal capacities for non-recyclable waste across Europe. As landfill restrictions tighten, WtE operators, especially in major markets like Germany, are compensating for declining domestic waste volumes by increasing imports from other European nations.
>>> All about EfW: ISWA White Book on Energy from Waste Technologies
Industry stability despite slight decline
While the overall sentiment in the broader WtE industry remains positive, it has softened slightly from 2023 levels. About 90% of industry companies report a stable or good business situation, though this is a slight dip from 94% in 2023. Order backlogs remain strong, with 75% of companies describing them as sufficient or high. Looking forward, more businesses anticipate favorable developments (29%) than unfavorable ones (14%), signaling continued stability.
Employment growth slows
Employment trends remain positive, though with less momentum than in previous years. Most operators and industry firms expect workforce numbers to remain stable or grow, but only 28% of industrial companies anticipate an increase in employment, down from 37% in 2023.
Rising gate fees and regulatory pressures
Financial pressures on the sector are increasing. Nearly half (49%) of WtE plant operators expect gate fees to rise in the next 12 months, compared to 45% in 2023. This trend is particularly pronounced in Germany, where a new CO2 levy on waste fuels introduced in January 2024 is expected to escalate in the coming years.
Challenges in carbon management implementation
Carbon management remains a key discussion point in the industry, with 61% of plant operators exploring CO2 capture and storage solutions. However, only 14% have committed to developing such infrastructure, highlighting the challenges of high investment costs (34%) and an inadequate legal framework (31%). Additionally, insufficient transport infrastructure for CO2 and unclear business models further hinder adoption.
Minimal impact from biowaste separation laws
The introduction of mandatory separate biowaste collection under Article 22 of the EU Waste Framework Directive in 2024 has had little impact on WtE plant operators. A majority (63%) report no expected reduction in waste volumes for thermal treatment, particularly in countries like Germany that had already implemented similar measures. Only 28% anticipate a decline in available waste due to this policy.
Geographic trends: European market remains key
Europe continues to be the core market for the WtE industry, while interest in China and other Asian markets has waned due to economic instability, particularly China’s real estate crisis. In contrast, Australia and the Middle East are gaining attention as emerging markets. However, expansion into regions like India and Brazil remains challenging due to weak financial incentives, regulatory hurdles, and the prevalence of landfilling.
With Europe’s aging WtE infrastructure, the focus is shifting from new plant construction to maintenance and modernization, a trend that is expected to persist in the coming years.


